Bioassay Development and toxicology screening
The cell production and differentiation expertise of CTIBIOTECH has been applied to creating unique and sensitive toxicology and drug-response bioassays in conjunction with major pharmaceutical actors.
Primary work includes:
- hepatic cell toxicology testing
- neural cell responsiveness testing
- neural cell responsiveness testing
- intradermal cell responsiveness
CTIBIOTECH is able to set up bioassay and specific tests to specification and has developed high-throughput screening of difficult models for the in vitro drug-screening and components industries.
To discuss this work, contact us here
 PROJECT: development of neural response to defined modulators.
PROJECT: development of neural response to defined modulators.
Abstract of work presented at conference:
Assessment of Neurogenic Properties of Five Plant Extracts.
S. Pain, N. Forraz, G. Atzeni, C. McGuckin, N. Bechetoille
BASF. CTIBIOTECH
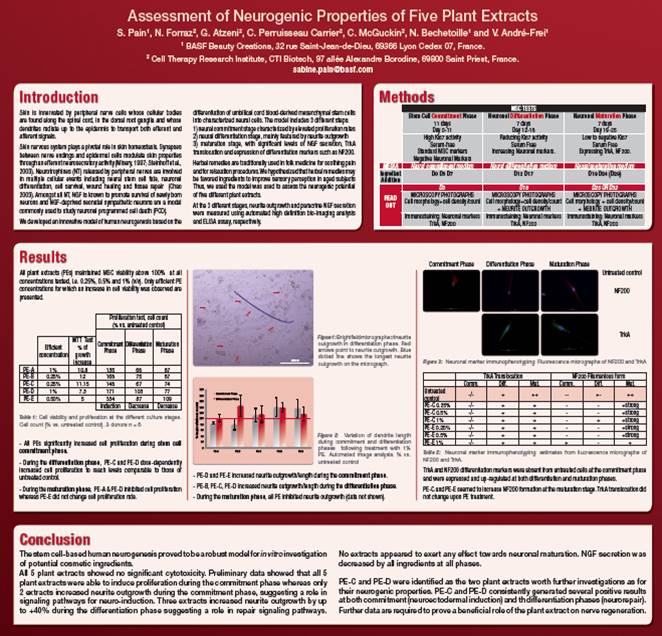
Skin is innervated by peripheral nerve cells whose cellular bodies are found along the spinal cord, in the dorsal root ganglia and whose dendrites radiate up to the epidermis to transport both efferent and afferent signals. Skin nervous system plays a pivotal role in skin homeostasis. Synapses between nerve endings and epidermal cells modulate skin properties through an efferent neurosecretory activity (Misery, 1997; Steinhoff et al., 2003). Neurotrophines (NT) released by peripheral nerves are involved in multiple cellular events including neural stem cell fate, neuronal differentiation, cell survival, wound healing and tissue repair (Chao 2003). Amongst all NT, NGF is known to promote survival of newly born neurons and NGF-deprived neonatal sympathetic neurons are a model commonly used to study neuronal programmed cell death (PCD). We developed an innovative model of human neurogenesis based on the differentiation of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into characterized neural cells. The model includes 3 different steps: 1) neural commitment stage characterized by elevated proliferation rates 2) neural differentiation stage, mainly featured by neurite outgrowth 3) maturation stage, with significant levels of NGF secretion, TrkA translocation and expression of differentiation markers such as NF200. Herbal remedies are traditionally used in folk medicine for soothing pain and for relaxation procedures. We hypothesized that herbal remedies may be favored ingredients to improve sensory perception in aged subjects Thus, we used the model was used to assess the neurogenic potential of five different plant extracts. At the 3 different stages, neurite outgrowth and paracrine NGF secretion were measured using automated high definition bio-imaging analysis and ELISA assay, respectively. CONCLUSION: The stem cell-based human neurogenesis proved to be a robust model for in vitro investigation of potential cosmetic ingredients. All 5 plant extracts showed no significant cytotoxicity. Preliminary data showed that all 5 plant extracts were able to induce proliferation during the commitment phase whereas only 2 extracts increased neurite outgrowth during the commitment phase, suggesting a role in signaling pathways for neuro-induction. Three extracts increased neurite outgrowth by up to +40% during the differentiation phase suggesting a role in repair signaling pathways. No extracts appeared to exert any effect towards neuronal maturation. NGF secretion was decreased by all ingredients at all phases. PE-C and PE-D were identified as the two plant extracts worth further investigations as for their neurogenic properties. PE-C and PE-D consistently generated several positive results at both commitment (neuroectodermal induction) and th differentiation phases (neurorepair). Further data are required to prove a beneficial role of the plant extract on nerve regeneration.